node_similarity
Abstract
If we're interested in how similar two nodes in a graph are, we'll want to get a numerical value that represents the node similarity between those two nodes. There are many node similarity measures and currently this module contains the following:
- cosine similarity
- Jaccard similarity
- overlap similarity
The Jaccard similarity is computed using the following formula:
The overlap similarity is computed using the following formula:
The cosine similarity computes similarity between two nodes based on some property. This property should be a vector and it can be computed using the following formula:
Set A represents all outgoing neighbors of one node, set B represents all outgoing neighbors of the other node. In all the given formulas, the numerator is the cardinality of the intersection of set A and set B (in other words, the cardinality of the common neighbors set). The denominator differs but requires the cardinality of sets A and B in some way.
For each similarity measure, there are two functions, one that calculates similarity between all pairs of nodes and the other, pairwise function, that takes into account pairwise similarities between two set of nodes.
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | directed |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
If you want to execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph, be sure to check out the guide on How to run a MAGE module on subgraphs.
cosine()
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The cosine similarity between the first and the second node.
Usage:
CALL node_similarity.cosine() YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity
cosine_pairwise(src_nodes, dst_nodes)
Input:
src_nodes: List[Vertex]➡ The first set of nodes.dst_nodes: List[Vertex]]➡ The second set of nodes.property: str➡ The property based on which the cosine similarity will be calculated. If the property is not of the vector type, the error will be thrown.
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The cosine similarity between the first and the second node.
Usage:
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id < 8
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.cosine_pairwise("score", nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity
jaccard()
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The Jaccard similarity between the first and the second node.
Usage:
CALL node_similarity.jaccard() YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity;
jaccard_pairwise(src_nodes, dst_nodes)
Input:
src_nodes: List[Vertex]➡ The first set of nodes.dst_nodes: List[Vertex]➡ The second set of nodes.
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The Jaccard similarity between the first and the second node.
Usage:
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id < 8
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.jaccard_pairwise(nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity
overlap()
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The overlap similarity between the first and the second node.
Usage:
CALL node_similarity.overlap() YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity;
overlap_pairwise(node1, node2)
Input:
src_nodes: List[Vertex]➡ The first set of nodes.dst_nodes: List[Vertex]➡ The second set of nodes.
Output:
node1: Vertex➡ The first node.node2: Vertex➡ The second node.similarity: float➡ The overlap similarity between the first and the second node.
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id < 8
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.overlap_pairwise(nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity
RETURN node1, node2, similarity;
Example - cosine pairwise similarity
- Step 1: Input graph
- Step 2: Cypher load commands
- Step 3: Running command
- Step 4: Results
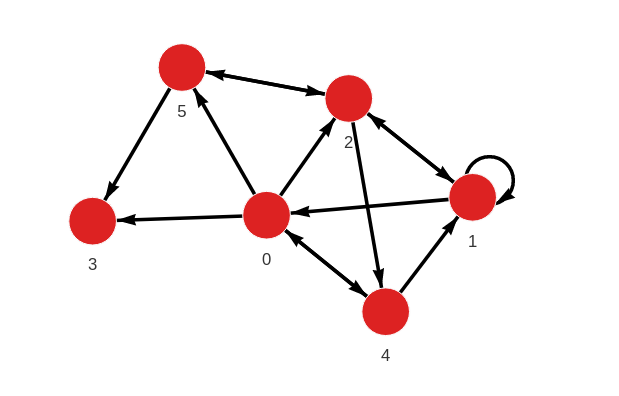
CREATE (b:Node {id: 0, score: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]});
CREATE (b:Node {id: 1, score: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]});
CREATE (b:Node {id: 2, score: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]});
CREATE (b:Node {id: 3, score: [1.0, 1.0, 0.0]});
CREATE (b:Node {id: 4, score: [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]});
CREATE (b:Node {id: 5, score: [1.0, 0.0, 1.0]});
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id < 3
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.cosine_pairwise("score", nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity AS cosine_similarity
RETURN node1, node2, cosine_similarity;
+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| node1 | node2 | cosine_similarity |
+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+
| (:Node {id: 1}) | (:Node {id: 3}) | 0.816 |
| (:Node {id: 2}) | (:Node {id: 4}) | 0.577 |
| (:Node {id: 0}) | (:Node {id: 5}) | 0.816 |
+-------------------+-------------------+-------------------+
Example - Jaccard pairwise similarity
- Step 1: Input graph
- Step 2: Cypher load commands
- Step 3: Running command
- Step 4: Results

MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id < 3
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.jaccard_pairwise(nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity AS jaccard_similarity
RETURN node1, node2, jaccard_similarity;
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
| node1 | node2 | jaccard_similarity |
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
| (:Node {id: 1}) | (:Node {id: 3}) | 0.0 |
| (:Node {id: 2}) | (:Node {id: 4}) | 0.25 |
| (:Node {id: 0}) | (:Node {id: 5}) | 0.5 |
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
Example - overlap similarity
- Step 1: Input graph
- Step 2: Cypher load commands
- Step 3: Running command
- Step 4: Results

MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MATCH (m)
WHERE m.id < 3
WITH COLLECT(m) AS nodes1
MATCH (n)
WHERE n.id > 2
WITH COLLECT(n) AS nodes2, nodes1
CALL node_similarity.overlap_pairwise(nodes1, nodes2) YIELD node1, node2, similarity AS overlap_similarity
RETURN node1, node2, overlap_similarity;
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
| node1 | node2 | overlap_similarity |
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
| (:Node {id: 1}) | (:Node {id: 3}) | 0.0 |
| (:Node {id: 2}) | (:Node {id: 4}) | 0.5 |
| (:Node {id: 0}) | (:Node {id: 5}) | 1.0 |
+-------------------+-------------------+--------------------+
