degree_centrality
Degree Centrality is the basic measurement of centrality that refers to the number of edges adjacent to a node. For directed graphs, we define an in-degree measure, which is defined as the number of in-coming edges, and an out-degree measure, defined as the number of out-going edges.
Let $A = (a{i,j})$ be the adjacency matrix of a directed graph. The in-degree centrality $x{i}$ of node $i$ is given by: $$x{i} = \sum_k a{k,i}$$ or in matrix form (1 is a vector with all components equal to unity): $$x = 1 A$$ The out-degree centrality $y{i}$ of node $i$ is given by: $$y{i} = \sumk a{i,k}$$ or in matrix form: $$y = A 1$$
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | directed/undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | sequential |
Procedures
If you want to execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph, be sure to check out the guide on How to run a MAGE module on subgraphs.
get(type)
Output:
node➡ Node in the graph, for which Degree Centrality is calculated.degree➡ Calculated degree of a node.
Usage:
CALL degree_centrality.get()
YIELD node, degree;
get_subgraph(nodes, relationships, type)
Input:
nodes: list[node]➡ nodes to be used in the algorithm.relationships: list[relationship]➡ relationships to be considered for degree calculation.type: string (default="undirected")➡ whether we are using "in", "out", or "undirected" edges.
Output:
node➡ Node in the graph, for which Degree Centrality is calculated.degree➡ Calculated degree of a node.
Usage:
CALL degree_centrality.get()
YIELD node, degree;
Example
- Step 1: Input graph
- Step 2: Cypher load commands
- Step 3: Running command
- Step 4: Results
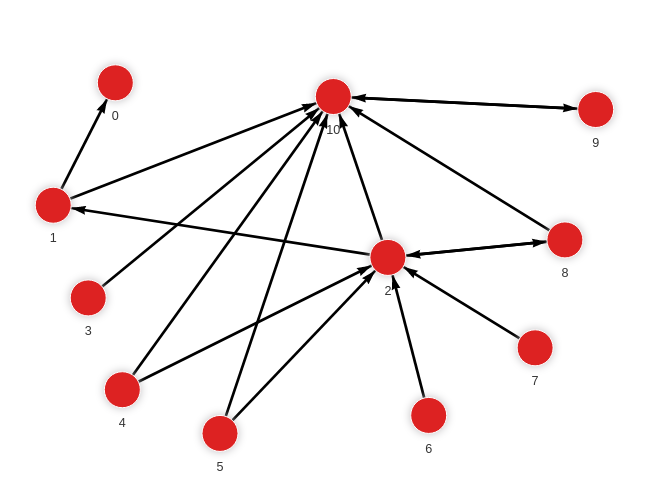
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 0}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 8}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 5}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 6}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 7}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 8}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 9}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 10}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a:Node {id: 10}) MERGE (b:Node {id: 9}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
CALL degree_centrality.get("in")
YIELD node, degree
RETURN node, degree;
+------------------+------------------+
| node | degree |
+------------------+------------------+
| (:Node {id: 9}) | 1 |
| (:Node {id: 7}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 6}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 5}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 4}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 3}) | 0 |
| (:Node {id: 8}) | 1 |
| (:Node {id: 2}) | 5 |
| (:Node {id: 10}) | 7 |
| (:Node {id: 0}) | 1 |
| (:Node {id: 1}) | 1 |
+------------------+------------------+
