betweenness_centrality_online
Betweenness centrality is among the most common metrics in graph analytics owing to its utility in identifying critical vertices of graphs. It is one of the tools in centrality analysis, a set of techniques for measuring the importance of nodes in networks.
The notion of Betweenness centrality is based on shortest paths: the shortest path between two nodes is the one consisting of the fewest edges, or in case of weighted graphs, the one with the smallest total edge weight. A node’s betweenness centrality is defined as the share of all shortest paths in the graph that run through it.
This query module delivers a fully dynamic betweenness centrality computation tool using the iCentral 1 algorithm by Jamour, Skiadopoulos and Kalnis. iCentral saves up on computation in two ways: it singles out the nodes whose centrality scores could have changed and then incrementally updates their scores, making use of previously calculated data structures where applicable.
This drives down the algorithm’s time complexity to O(m′n′) and space complexity to O(m + n), where m and n are the counts of edges and vertices in the graph, m′ is the number of edges in the biconnected component affected by the graph update, and n′ is the size of a subset of the nodes in the biconnected component. Consequently, the algorithm is suitable for mid-scale graphs.
Dynamic algorithms such as iCentral are especially suited for graph streaming solutions such as Memgraph. As updates arrive in a stream, the algorithm avoids redundant work by processing only the portion of the graph affected by the update.
1 Parallel Algorithm for Incremental Betweenness Centrality on Large Graphs (Jamour et al., 2017)
| Trait | Value |
|---|---|
| Module type | algorithm |
| Implementation | C++ |
| Graph direction | undirected |
| Edge weights | unweighted |
| Parallelism | parallel |
Procedures
If you want to execute this algorithm on graph projections, subgraphs or portions of the graph, be sure to check out the guide on How to run a MAGE module on subgraphs.
set(normalize, threads)
Input:
normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.threads: integer (default=Nº of concurrent threads supported by the implementation)➡ The number of threads used in calculating betweenness centrality.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.set()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;
get(normalize)
Input:
normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;
update(created_vertices, created_edges, deleted_vertices, deleted_edges, normalize, threads)
created_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices created in the latest graph update.created_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges created in the latest graph update.updated_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices updated in the latest graph update.updated_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges updated in the latest graph update.deleted_vertices: List[Vertex]➡ Vertices deleted in the latest graph update.deleted_edges: List[Edge]➡ Edges deleted in the latest graph update.normalize: boolean (default=True)➡ IfTrue, the betweenness values are normalized by2/((n-1)(n-2)), wherenis the number of nodes in the graph.threads: integer (default=Nº of concurrent threads supported by the implementation)➡ The number of threads used in updating betweenness centrality.
Output:
node: Vertex➡ Graph vertex.betweenness_centrality: float➡ Betweenness centrality score of the above vertex.
Usage:
As there is a total of four complex obligatory parameters, setting the parameters by hand might be cumbersome. The recommended use of this method is to call it within a trigger, making sure beforehand that all predefined variables are available:
CREATE TRIGGER sample_trigger BEFORE COMMIT
EXECUTE CALL betweenness_centrality_online.update(createdVertices, createdEdges, deletedVertices, deletedEdges, normalize, threads) YIELD *;
Communities calculated by update() are accessible by subsequently calling
get():
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get()
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality;
Example
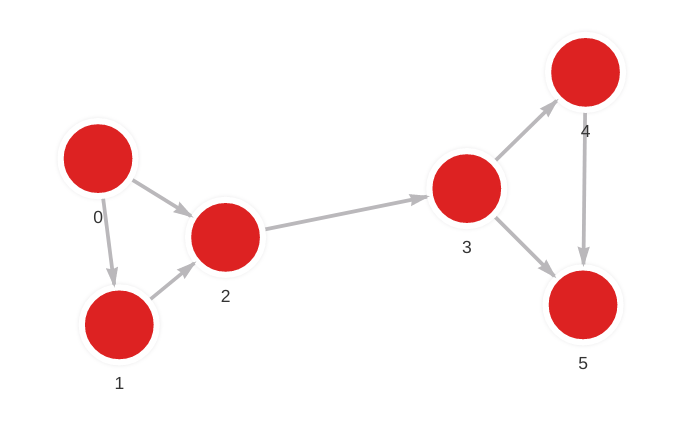
- Step 1: Input graph
- Step 2: Set trigger
- Step 3: Cypher load commands
- Step 4: Running command
- Step 5: Results
CREATE TRIGGER update_bc_trigger
BEFORE COMMIT EXECUTE
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.update(createdVertices, createdEdges, deletedVertices, deletedEdges)
YIELD *;
MERGE (a: Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 1}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 0}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 1}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 2}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 2}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 3}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 4}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 3}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
MERGE (a: Node {id: 4}) MERGE (b: Node {id: 5}) CREATE (a)-[:RELATION]->(b);
CALL betweenness_centrality_online.get(True)
YIELD node, betweenness_centrality
RETURN node.id AS node_id, betweenness_centrality
ORDER BY node_id;
┌─────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┐
│ node_id │ betweenness_centrality │
├─────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ 0 │
│ 1 │ 0 │
│ 2 │ 0.6 │
│ 3 │ 0.6 │
│ 4 │ 0 │
│ 5 │ 0 │
└─────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────┘
