How to use the NetworkX library with Memgraph
NetworkX is a Python package for the creation, manipulation, and study of the structure,
dynamics, and functions of complex networks. Memgraph has nxalg query module, which is a wrapper around NetworkX graph algorithms. It also provides Graph Analyzer query module, which utilizes the NetworkX library. Besides that, you can create a custom query module that uses the NetworkX library. Through this how-to guide, you can find out:
How to run NetworkX algorithms in Memgraph Lab
NetworkX algorithms are integrated into Memgraph as query modules inside Memgraph’s open-source graph extension library MAGE. Head over to the guide on how to call MAGE procedures to find out how to call all Memgraph procedures, including those that utilize the NetworkX library.
This how-to guide will show one simple example of calling a NetworkX procedure in Memgraph's visual interface Memgraph Lab.
1. Connect to Memgraph
First, run Memgraph using the Memgraph Platform Docker image, which includes both the MAGE library and Memgraph Lab. To run the image, open a command-line interpreter and run the following Docker command:
docker run -it -p 7687:7687 -p 7444:7444 -p 3000:3000 memgraph/memgraph-platform:latest
Connect to Memgraph via Memgraph Lab which is running at localhost:3000.
Check out the installation guide for other installation options. If you wish to avoid the installation, you can also use Memgraph Cloud.
2. Load the dataset
Head over to the Datasets section to load a dataset and load the Europe backpacking dataset.
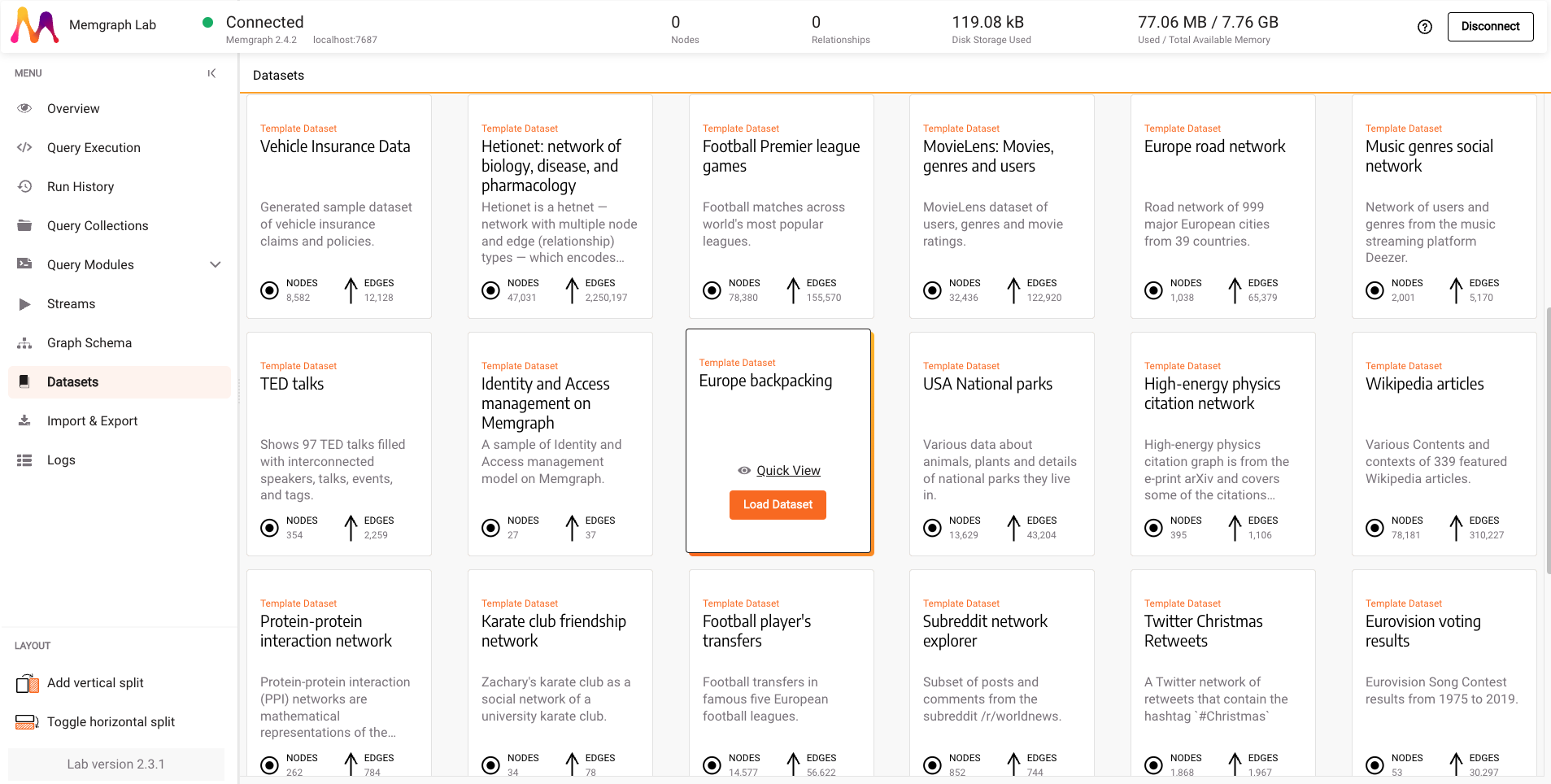
3. Run NetworkX algorithm
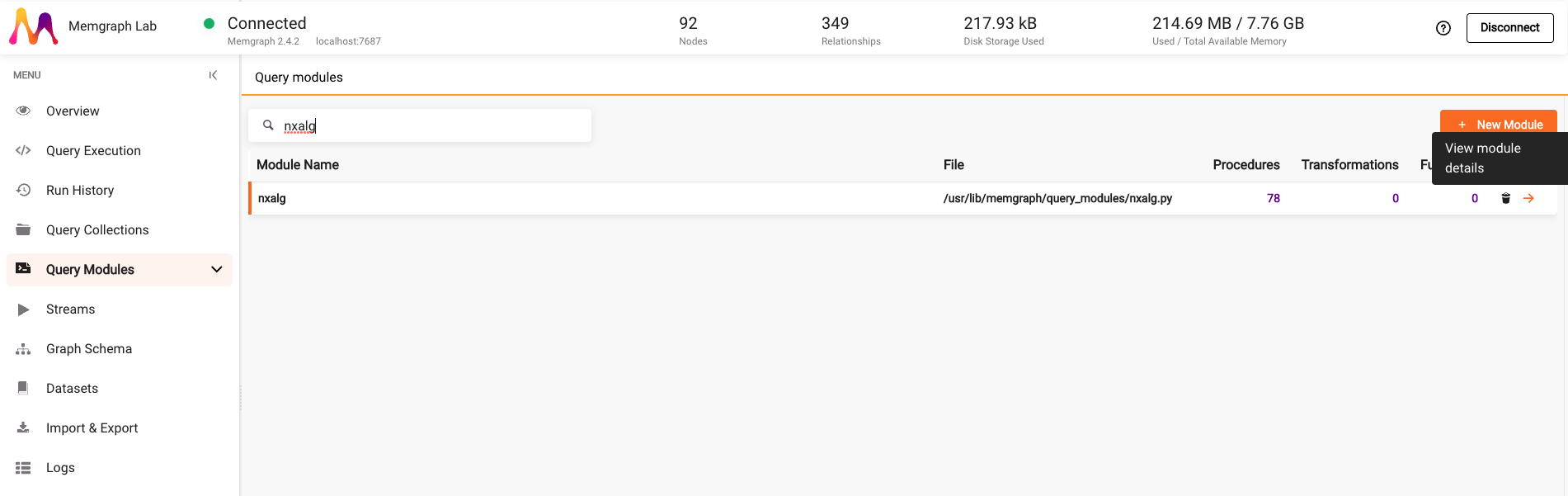
Once the dataset is loaded, go to the Query Modules section and search for nxalg module. Click on the arrow next to the module name to view module details.
The goal is to run the is_bipartite() procedure to check whether the graph is bipartite.
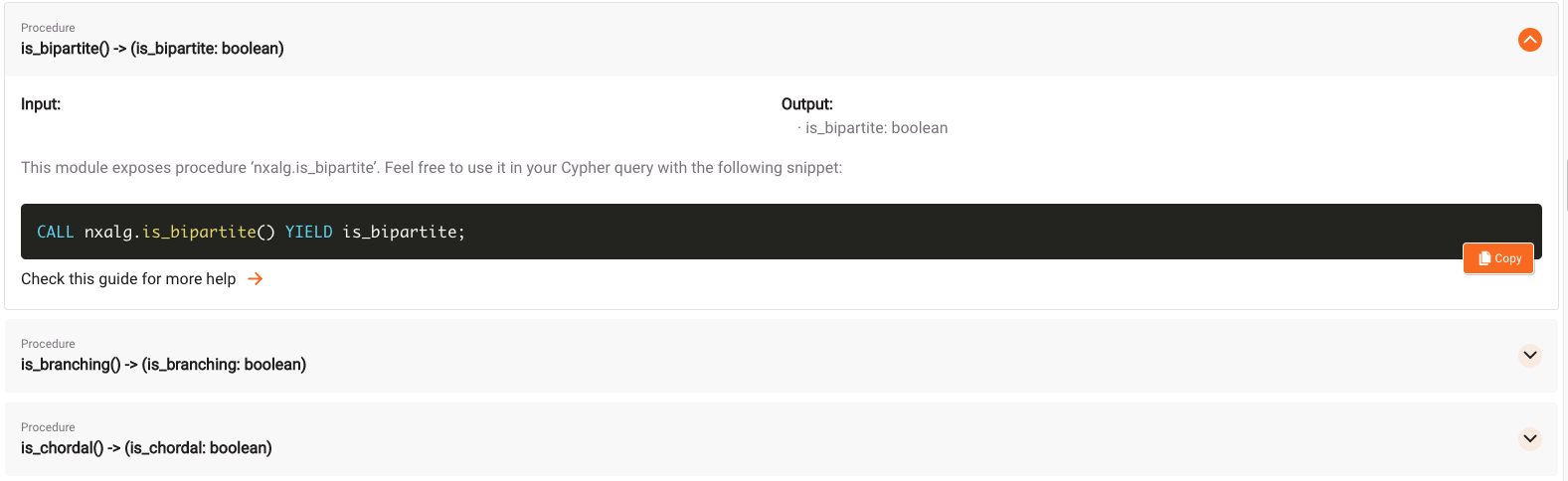
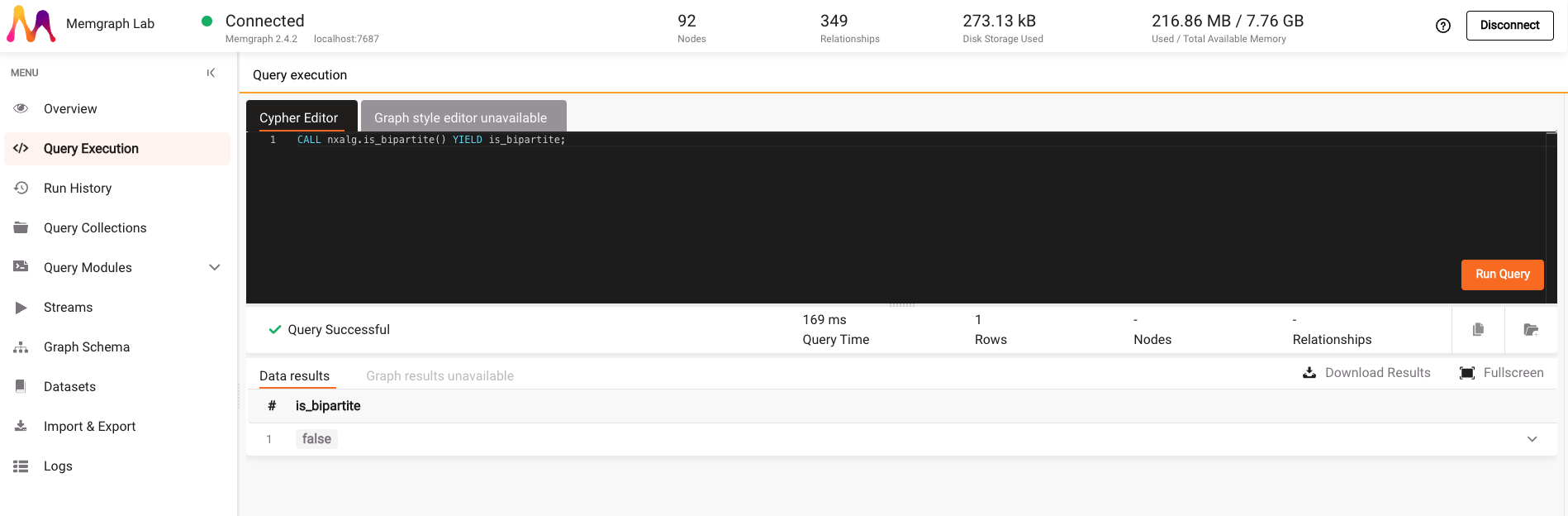
Copy the query, go to the Query Execution tab and paste the query into the Cypher Editor:
CALL nxalg.is_bipartite() YIELD is_bipartite;
By clicking on the Run Query button, you can see that the Europe backpacking graph is not bipartite.
In the same way, you can run other procedures from the nxalg module and the procedures from the graph_analyzer module, which can be found in the Query Modules section.
How to implement custom NetworkX module in Memgraph Lab
Besides using already implemented modules, you can create your own module which utilizes the NetworkX library. To learn how to implement a custom query module, head over to the example of query module in Python.
Since Memgraph is integrated with NetworkX, you can import NetworkX library inside Python code. This guide will show you how to create a new query module that utilizes the NetworkX library within Memgraph's visual interface Memgraph Lab.
1. Connect to Memgraph
First, run Memgraph using the Memgraph Platform Docker image, which includes both the MAGE library and Memgraph Lab. To run the image, open a command-line interpreter and run the following Docker command:
docker run -it -p 7687:7687 -p 7444:7444 -p 3000:3000 memgraph/memgraph-platform:latest
Connect to Memgraph via Memgraph Lab which is running at localhost:3000.
Check out the installation guide for other installation options. If you wish to avoid the installation, you can also use Memgraph Cloud.
2. Load the dataset
In the Datasets section, find and load the Karate club friendship network dataset.
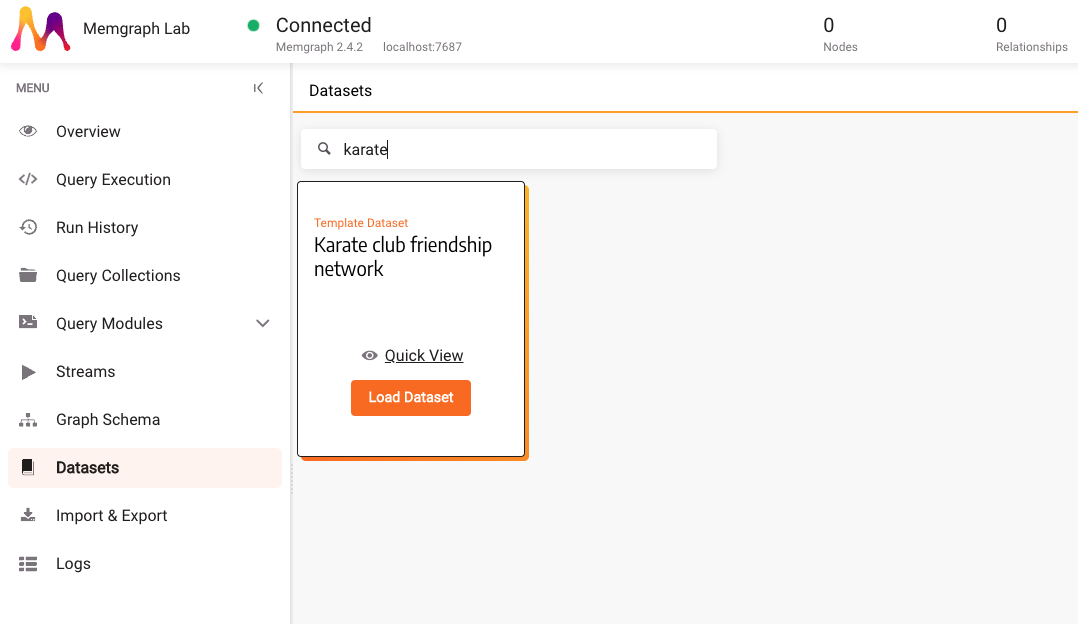
3. Implement a custom query module
Once the dataset is loaded, go to the Query modules section. The goal is to create a community detection algorithm that can partition a network into multiple communities with the help of the NetworkX library. Click on the New Module and type in the module name, e.g., communities.
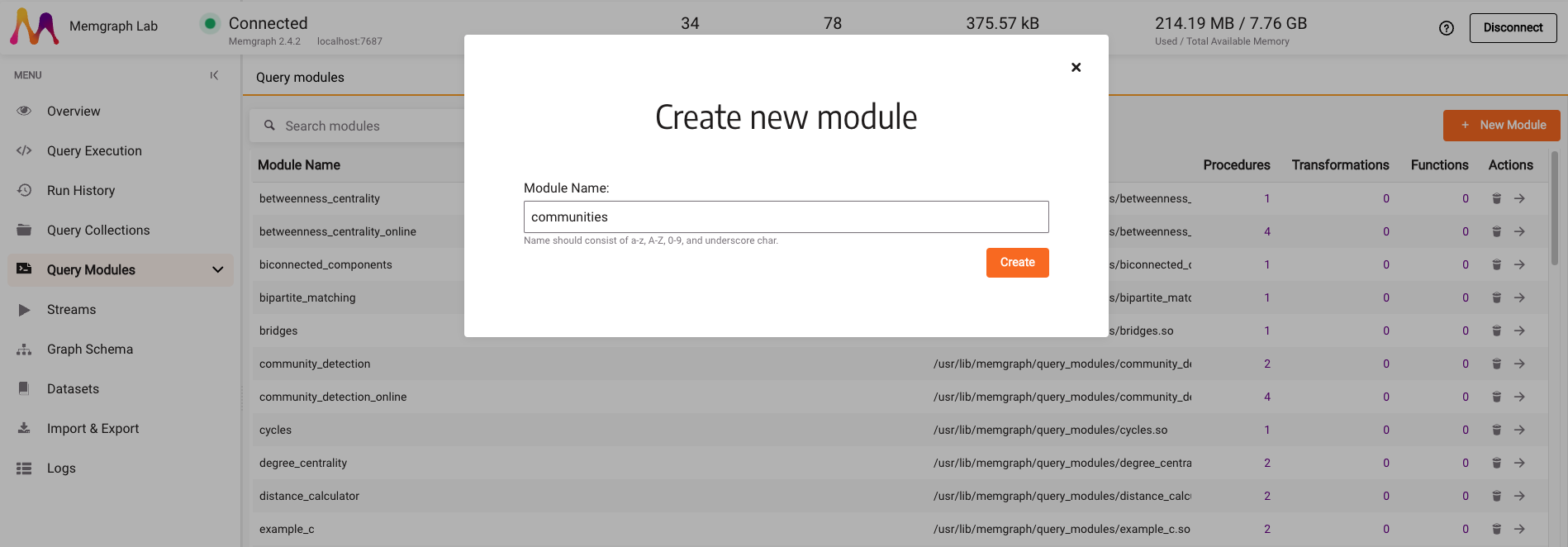
There is a sample Python code on the next screen, inside the code editor. Select it, delete it and paste the following code:
import mgp
import networkx as nx
from networkx.algorithms import community
from mgp_networkx import MemgraphDiGraph
@mgp.read_proc
def detect(
ctx: mgp.ProcCtx
) -> mgp.Record(communities=mgp.List[mgp.List[mgp.Vertex]]):
networkxGraph = nx.DiGraph(MemgraphDiGraph(ctx=ctx))
communities_generator = community.girvan_newman(networkxGraph)
return mgp.Record(communities=[
list(s) for s in next(communities_generator)])
In the above code we are creating a read procedure which creates a NetworkX DiGraph from the MemgraphDiGraph object which takes the existing graph from the database. After that, we run the Girvan-Newman community algorithm and return its results.
Here is what the code looks like in the code editor:
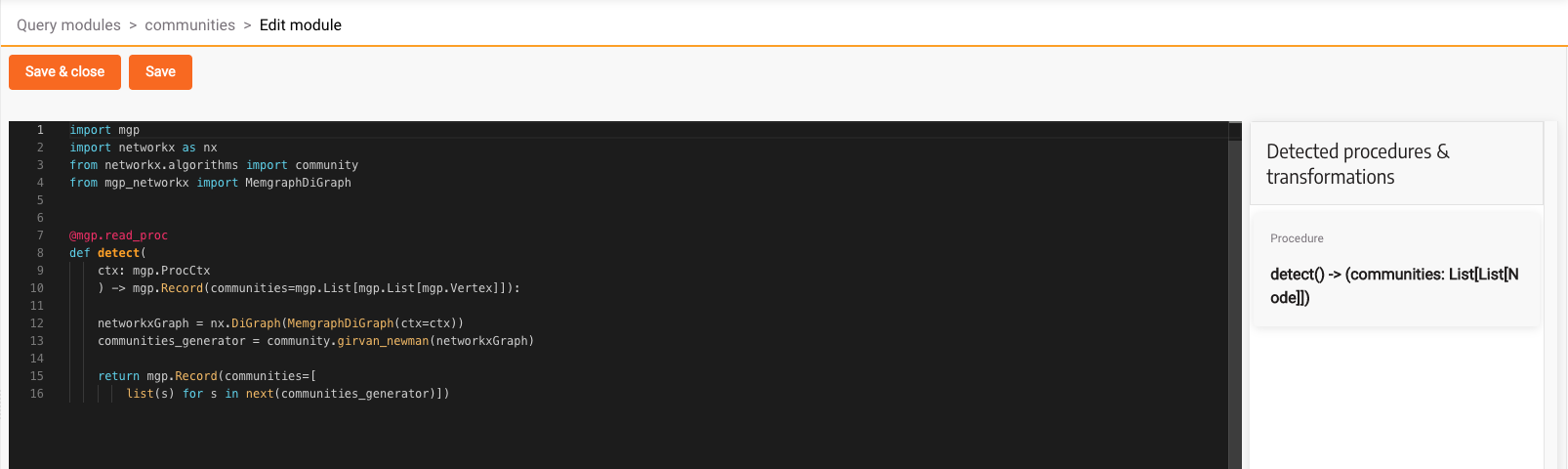
Click Save & close, and head over to the Query Execution tab.
4. Run the custom query module
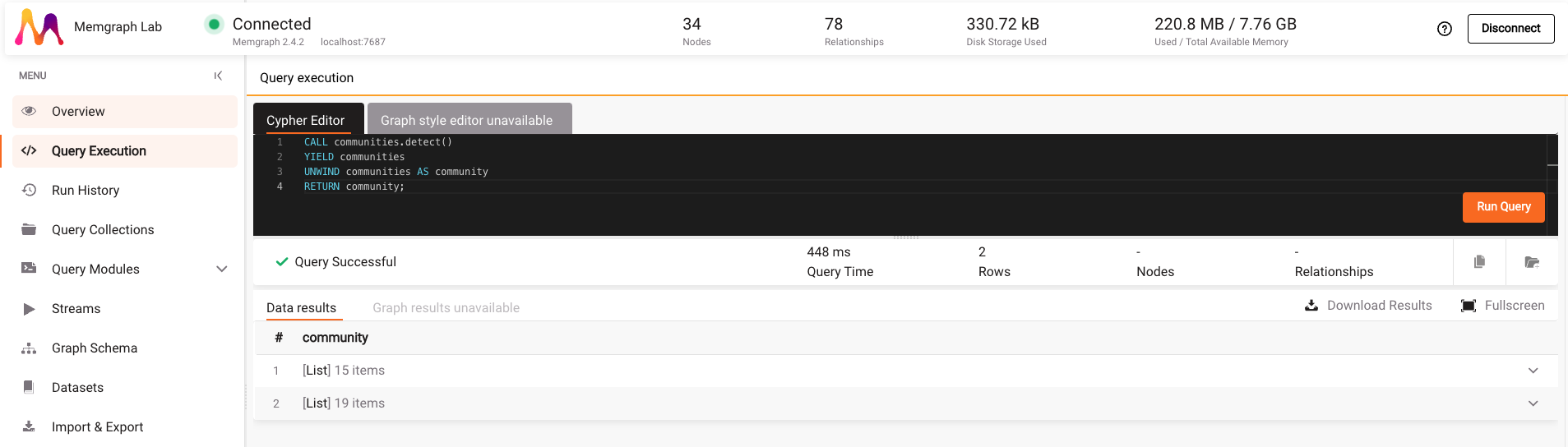
Copy and paste the following query to the Cypher Editor:
CALL communities.detect()
YIELD communities
UNWIND communities AS community
RETURN community;
After you click on Run Query, you can see the result, which consists of two lists. Each list represents one community.
Where to next?
If you want to learn more about how to use Memgraph with NetworkX, check out the Memgraph for NetworkX developers resources. If you are using GQLAlchemy to connect to Memgraph, learn how to import NetworkX graph into Memgraph in the how-to guide on GQLAlchemy documentation.