Elasticsearch queryedit
The Elasticsearch query rule type runs a user-configured query, compares the number of matches to a configured threshold, and schedules actions to run when the threshold condition is met.
Create the ruleedit
In Stack Management > Rules, click Create rule, fill in the name and optional tags, then select Elasticsearch query. An Elasticsearch query rule can be defined using KQL/Lucene or Query DSL.
Define the conditionsedit
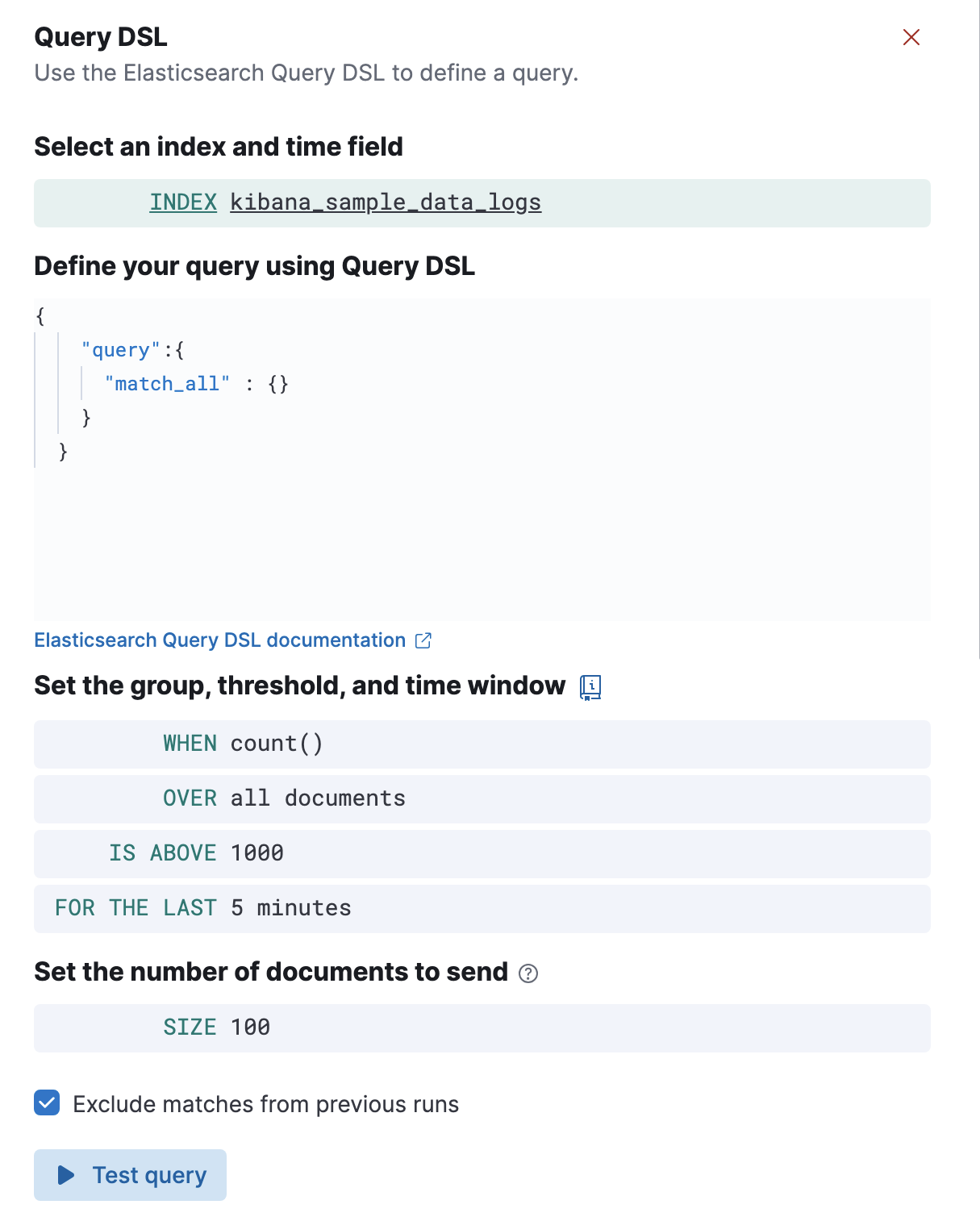
- Define your query
-
If you chose the query DSL option, you must specify indices to query and a time field that is used for the time window. You must then define a query in Elasticsearch query DSL. Only the
query,fields,_sourceandruntime_mappingsfields are used, other DSL fields are not considered.If you chose the KQL or Lucene option, you must specify a data view then define a text-based query.
- Set the group, theshold, and time window
-
- When
-
Specify how to calculate the value that is compared to the threshold. The value is calculated by aggregating a numeric field within the time window. The aggregation options are:
count,average,sum,min, andmax. When usingcountthe document count is used and an aggregation field is not necessary. - Over or Grouped Over
- Specify whether the aggregation is applied over all documents or split into groups using a grouping field. If grouping is used, an alert will be created for each group when it meets the condition. To limit the number of alerts on high cardinality fields, you must specify the number of groups to check against the threshold. Only the top groups are checked.
- Threshold
-
Defines a threshold value and a comparison operator (
is above,is above or equals,is below,is below or equals, oris between). The value calculated by the aggregation is compared to this threshold. - Time window
- Defines how far back to search for documents, using the time field set in the index clause. Generally this value should be set to a value higher than the check interval, to avoid gaps in detection.
- Set the number of documents to send
- Specifies the number of documents to pass to the configured actions when the threshold condition is met.
- Exclude matches from previous run
- Turn on to avoid alert duplication by excluding documents that have already been detected by the previous rule run. This option is not available when a grouping field is specified.
Add actionsedit
You can optionally send notifications when the rule conditions are met and when they are no longer met. In particular, this rule type supports:
- alert summaries
- actions that run when the query is matched
- recovery actions that run when the rule conditions are no longer met
For each action, you must choose a connector, which provides connection information for a Kibana service or third party integration. For more information about all the supported connectors, go to Connectors.
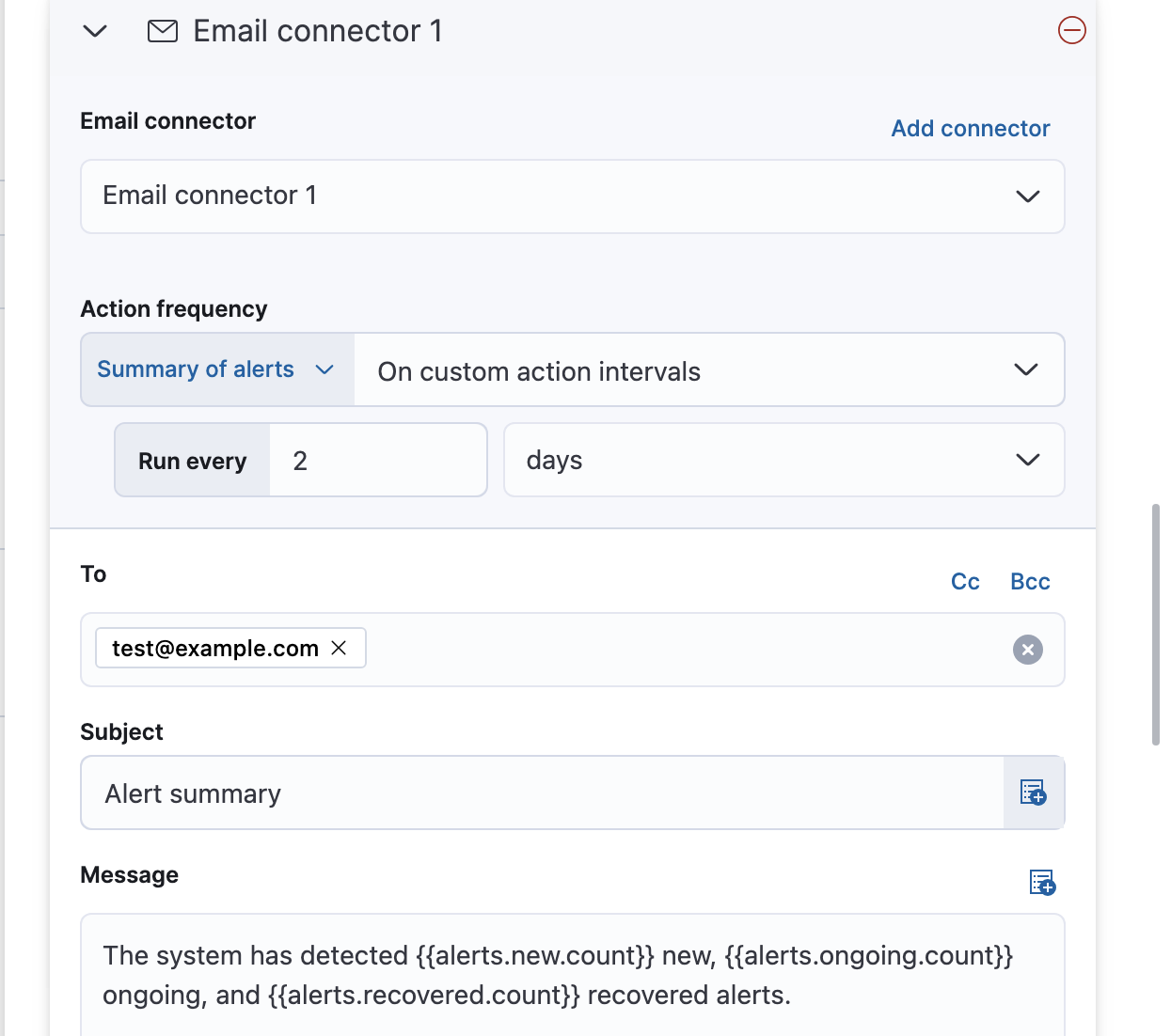
After you select a connector, you must set the action frequency. You can choose to create a summary of alerts on each check interval or on a custom interval. For example, send email notifications that summarize the new, ongoing, and recovered alerts at a custom interval:
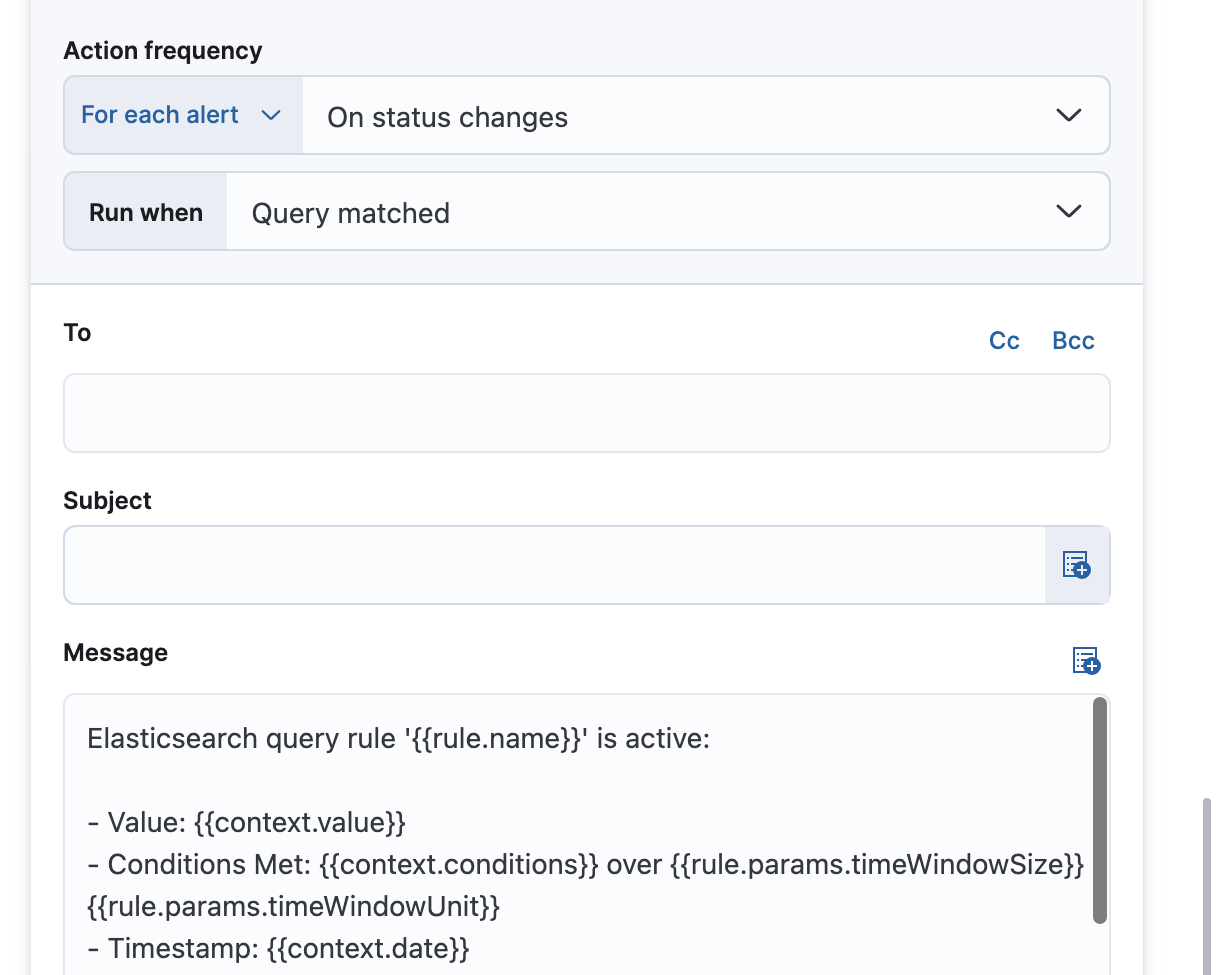
Alternatively, you can set the action frequency such that actions run for each alert. Choose how often the action runs (at each check interval, only when the alert status changes, or at a custom action interval). You must also choose an action group, which indicates whether the action runs when the query is matched or when the alert is recovered. For example:
Add action variablesedit
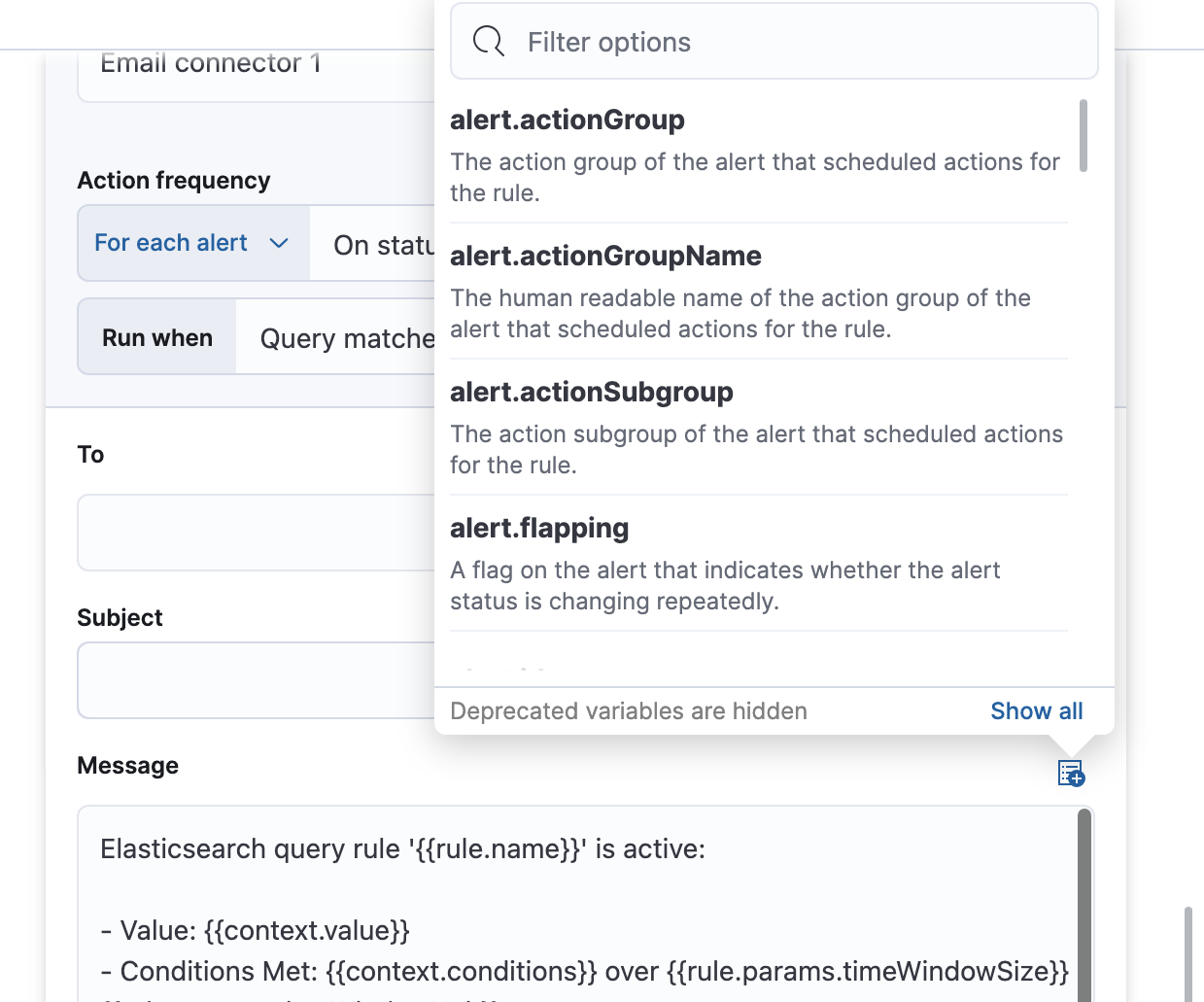
You can pass rule values to an action to provide contextual details. To view the list of variables available for each action, click the "add rule variable" button. For example:
The following variables are specific to the Elasticsearch query rule. You can also specify variables common to all rules.
-
context.title -
A preconstructed title for the rule. Example:
rule term match alert query matched. -
context.message -
A preconstructed message for the rule. Example:
rule 'my es-query' is active:
- Value: 2
- Conditions Met: Number of matching documents is greater than 1 over 5m
- Timestamp: 2022-02-03T20:29:27.732Z -
context.group -
The name of the action group associated with the condition.
Example:
query matched. -
context.date -
The date, in ISO format, that the rule met the condition.
Example:
2022-02-03T20:29:27.732Z. -
context.value - The value of the rule that met the condition.
-
context.conditions -
A description of the condition. Example:
count greater than 4. -
context.hits -
The most recent documents that matched the query. Using the Mustache template array syntax, you can iterate over these hits to get values from the Elasticsearch documents into your actions. For example, the message in an email connector action might contain:
Elasticsearch query rule '{{rule.name}}' is active: {{#context.hits}} Document with {{_id}} and hostname {{_source.host.name}} has {{_source.system.memory.actual.free}} bytes of memory free {{/context.hits}}The documents returned by
context.hitsinclude the_sourcefield. If the Elasticsearch query search API’sfieldsparameter is used, documents will also return thefieldsfield, which can be used to access any runtime fields defined by theruntime_mappingsparameter. For example:{{#context.hits}} timestamp: {{_source.@timestamp}} day of the week: {{fields.day_of_week}} {{/context.hits}}As the
fieldsresponse always returns an array of values for each field, the Mustache template array syntax is used to iterate over these values in your actions. For example:{{#context.hits}} Labels: {{#fields.labels}} - {{.}} {{/fields.labels}} {{/context.hits}}
Test your queryedit
Use the Test query feature to verify that your query DSL is valid.
-
Valid queries are run against the configured index using the configured time window. The number of documents that match the query is displayed.
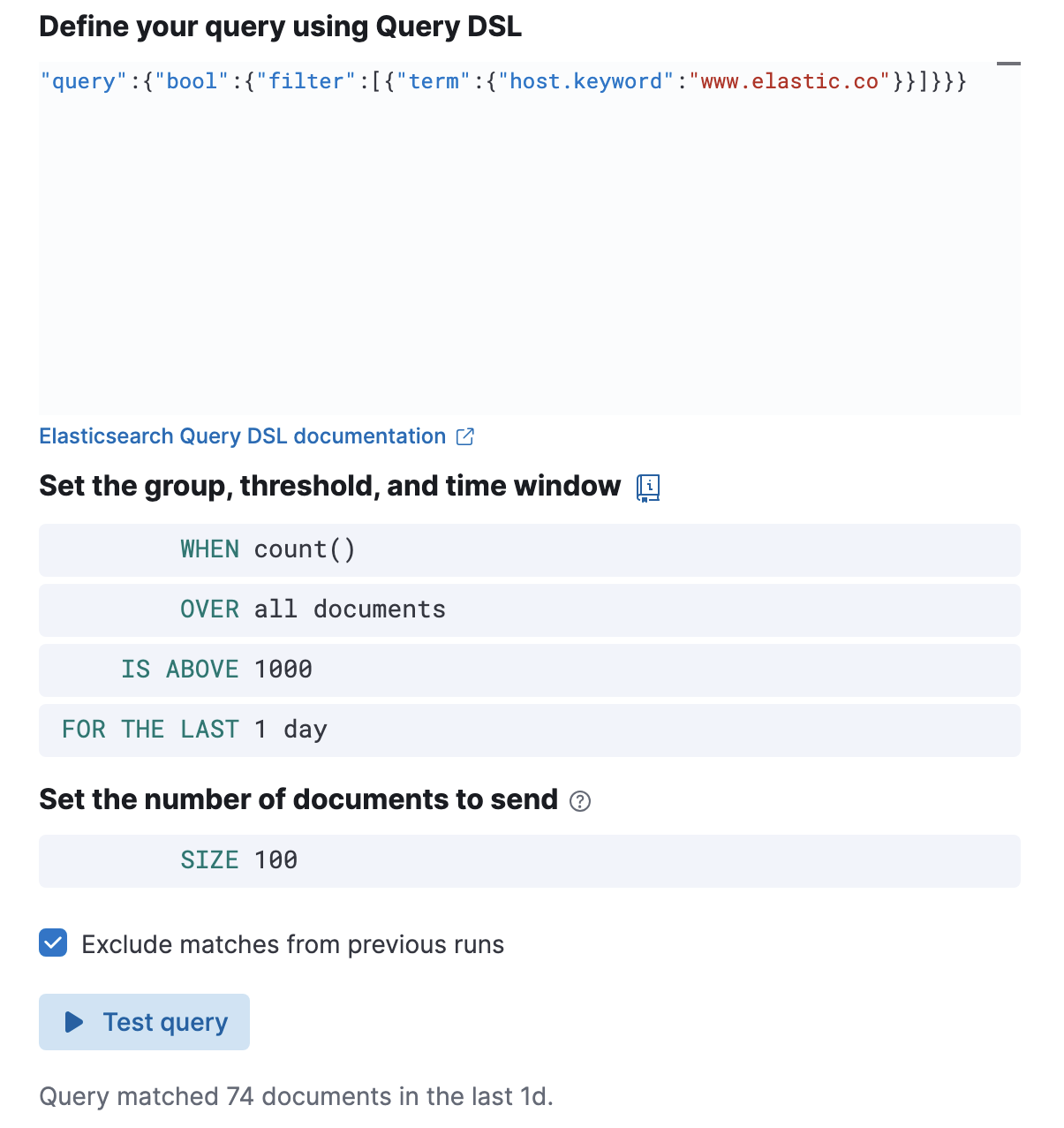
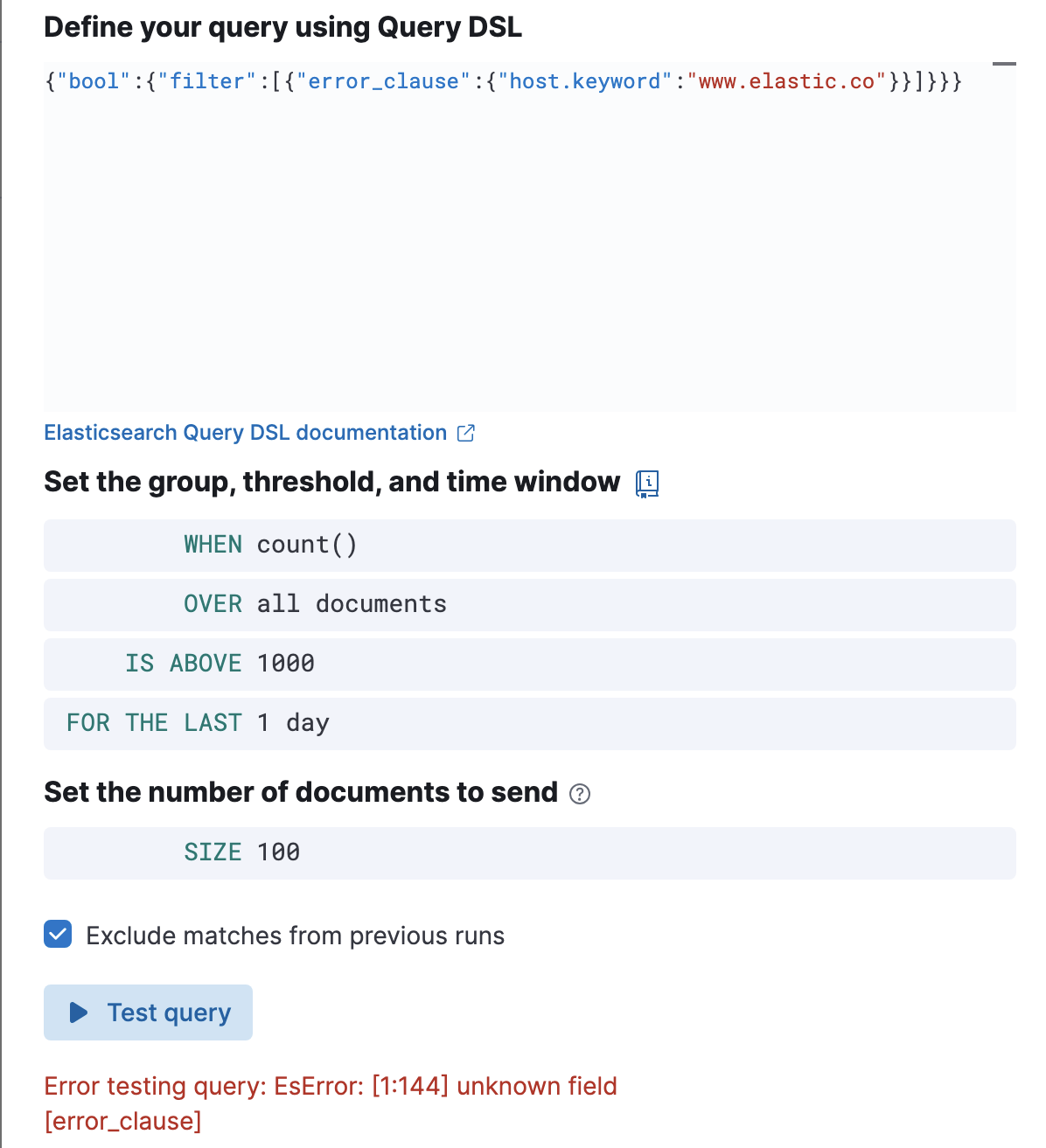
-
An error message is shown if the query is invalid.
Handling multiple matches of the same documentedit
By default, Exclude matches from previous run is turned on and the rule checks for duplication of document matches across multiple runs. If you configure the rule with a schedule interval smaller than the time window and a document matches a query in multiple runs, it is alerted on only once.
The rule uses the timestamp of the matches to avoid alerting on the same match multiple times. The timestamp of the latest match is used for evaluating the rule conditions when the rule runs. Only matches between the latest timestamp from the previous run and the current run are considered.
Suppose you have a rule configured to run every minute. The rule uses a time window of 1 hour and checks if there are more than 99 matches for the query. The Elasticsearch query rule type does the following:
|
Rule finds 113 matches in the last hour: |
Rule is active and user is alerted. |
|
Rule finds 127 matches in the last hour. 105 of the matches are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 22 matches: |
No alert. |
|
Rule finds 159 matches in the last hour. 88 of the matches are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 71 matches: |
No alert. |
|
Rule finds 190 matches in the last hour. 71 of them are duplicates that were already alerted on previously, so you actually have 119 matches: |
Rule is active and user is alerted. |