The LeViT model was proposed in LeViT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze. LeViT improves the Vision Transformer (ViT) in performance and efficiency by a few architectural differences such as activation maps with decreasing resolutions in Transformers and the introduction of an attention bias to integrate positional information.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
We design a family of image classification architectures that optimize the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency in a high-speed regime. Our work exploits recent findings in attention-based architectures, which are competitive on highly parallel processing hardware. We revisit principles from the extensive literature on convolutional neural networks to apply them to transformers, in particular activation maps with decreasing resolutions. We also introduce the attention bias, a new way to integrate positional information in vision transformers. As a result, we propose LeVIT: a hybrid neural network for fast inference image classification. We consider different measures of efficiency on different hardware platforms, so as to best reflect a wide range of application scenarios. Our extensive experiments empirically validate our technical choices and show they are suitable to most architectures. Overall, LeViT significantly outperforms existing convnets and vision transformers with respect to the speed/accuracy tradeoff. For example, at 80% ImageNet top-1 accuracy, LeViT is 5 times faster than EfficientNet on CPU.
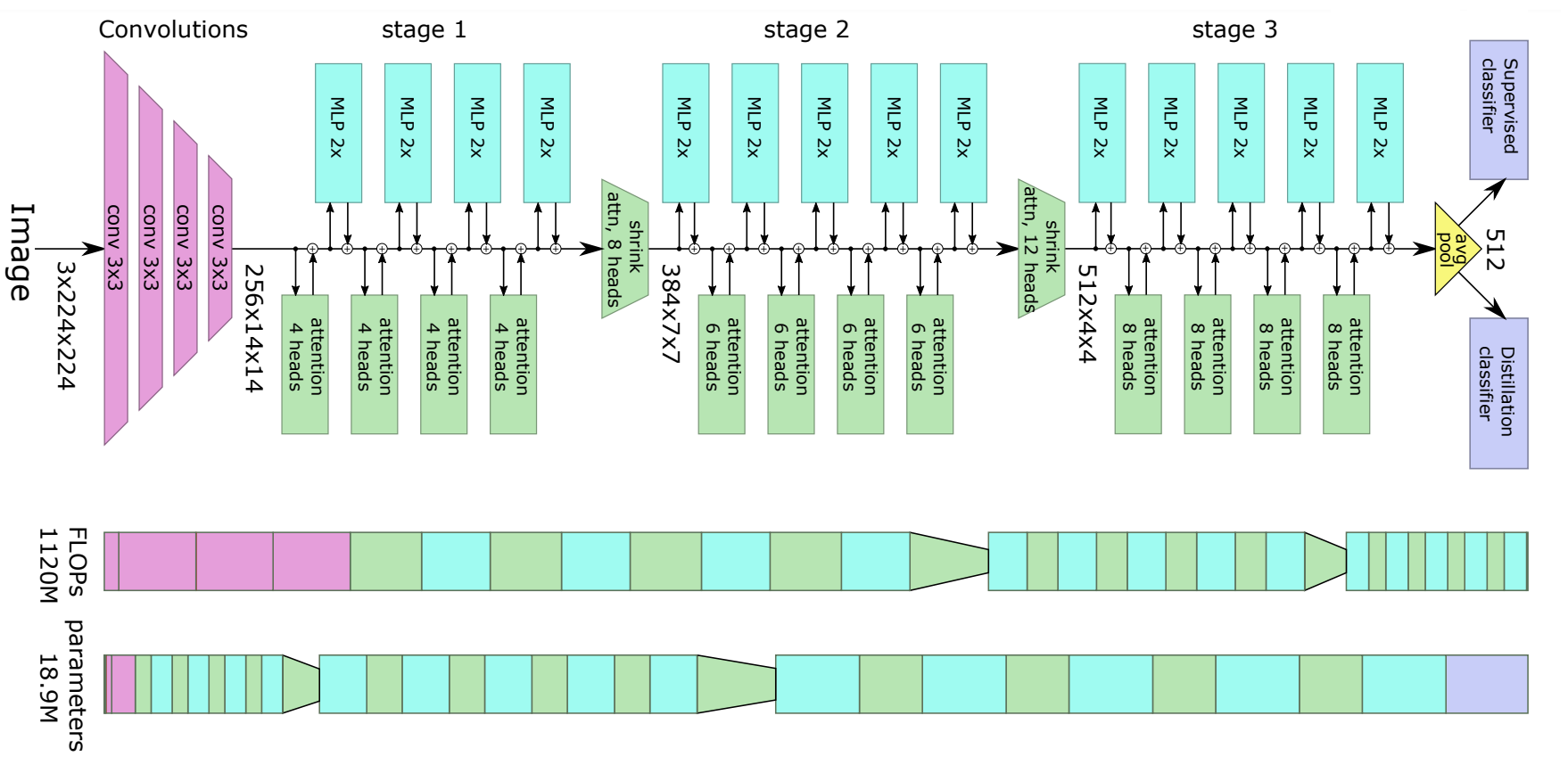 LeViT Architecture. Taken from the original paper.
LeViT Architecture. Taken from the original paper. This model was contributed by anugunj. The original code can be found here.
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with LeViT.
If you’re interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we’ll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
( image_size = 224 num_channels = 3 kernel_size = 3 stride = 2 padding = 1 patch_size = 16 hidden_sizes = [128, 256, 384] num_attention_heads = [4, 8, 12] depths = [4, 4, 4] key_dim = [16, 16, 16] drop_path_rate = 0 mlp_ratio = [2, 2, 2] attention_ratio = [2, 2, 2] initializer_range = 0.02 **kwargs )
Parameters
int, optional, defaults to 224) —
The size of the input image. int, optional, defaults to 3) —
Number of channels in the input image. int, optional, defaults to 3) —
The kernel size for the initial convolution layers of patch embedding. int, optional, defaults to 2) —
The stride size for the initial convolution layers of patch embedding. int, optional, defaults to 1) —
The padding size for the initial convolution layers of patch embedding. int, optional, defaults to 16) —
The patch size for embeddings. List[int], optional, defaults to [128, 256, 384]) —
Dimension of each of the encoder blocks. List[int], optional, defaults to [4, 8, 12]) —
Number of attention heads for each attention layer in each block of the Transformer encoder. List[int], optional, defaults to [4, 4, 4]) —
The number of layers in each encoder block. List[int], optional, defaults to [16, 16, 16]) —
The size of key in each of the encoder blocks. int, optional, defaults to 0) —
The dropout probability for stochastic depths, used in the blocks of the Transformer encoder. List[int], optional, defaults to [2, 2, 2]) —
Ratio of the size of the hidden layer compared to the size of the input layer of the Mix FFNs in the
encoder blocks. List[int], optional, defaults to [2, 2, 2]) —
Ratio of the size of the output dimension compared to input dimension of attention layers. float, optional, defaults to 0.02) —
The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a LevitModel. It is used to instantiate a LeViT model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the LeViT facebook/levit-128S architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PretrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PretrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import LevitConfig, LevitModel
>>> # Initializing a LeViT levit-128S style configuration
>>> configuration = LevitConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the levit-128S style configuration
>>> model = LevitModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configPreprocess an image or a batch of images.
( do_resize: bool = True size: Dict = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3> do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: Dict = None do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: Union = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: Union = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] image_std: Union = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] **kwargs )
Parameters
bool, optional, defaults to True) —
Wwhether to resize the shortest edge of the input to int(256/224 *size). Can be overridden by the
do_resize parameter in the preprocess method. Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to {"shortest_edge" -- 224}):
Size of the output image after resizing. If size is a dict with keys “width” and “height”, the image will
be resized to (size["height"], size["width"]). If size is a dict with key “shortest_edge”, the shortest
edge value c is rescaled to int(c * (256/224)). The smaller edge of the image will be matched to this
value i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to (size["shortest_egde"] * height / width, size["shortest_egde"]). Can be overridden by the size parameter in the preprocess method. PILImageResampling, optional, defaults to Resampling.BICUBIC) —
Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by the resample parameter in the
preprocess method. bool, optional, defaults to True) —
Whether or not to center crop the input to (crop_size["height"], crop_size["width"]). Can be overridden
by the do_center_crop parameter in the preprocess method. Dict, optional, defaults to {"height" -- 224, "width": 224}):
Desired image size after center_crop. Can be overridden by the crop_size parameter in the preprocess
method. bool, optional, defaults to True) —
Controls whether to rescale the image by the specified scale rescale_factor. Can be overridden by the
do_rescale parameter in the preprocess method. int or float, optional, defaults to 1/255) —
Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by the rescale_factor parameter in the
preprocess method. bool, optional, defaults to True) —
Controls whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by the do_normalize parameter in the
preprocess method. List[int], optional, defaults to [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) —
Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of
channels in the image. Can be overridden by the image_mean parameter in the preprocess method. List[int], optional, defaults to [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) —
Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the
number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by the image_std parameter in the preprocess method. Constructs a LeViT image processor.
( images: Union do_resize: Optional = None size: Optional = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: Optional = None crop_size: Optional = None do_rescale: Optional = None rescale_factor: Optional = None do_normalize: Optional = None image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None return_tensors: Optional = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: Union = None **kwargs )
Parameters
ImageInput) —
Image or batch of images to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging
from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, set do_rescale=False. bool, optional, defaults to self.do_resize) —
Whether to resize the image. Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to self.size) —
Size of the output image after resizing. If size is a dict with keys “width” and “height”, the image
will be resized to (height, width). If size is a dict with key “shortest_edge”, the shortest edge value
c is rescaled to int(c (256/224)). The smaller edge of the image will be matched to this value
i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to (size height / width, size). PILImageResampling, optional, defaults to PILImageResampling.BICUBIC) —
Resampling filter to use when resiizing the image. bool, optional, defaults to self.do_center_crop) —
Whether to center crop the image. Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to self.crop_size) —
Size of the output image after center cropping. Crops images to (crop_size[“height”],
crop_size[“width”]). bool, optional, defaults to self.do_rescale) —
Whether to rescale the image pixel values by rescaling_factor - typical to values between 0 and 1. float, optional, defaults to self.rescale_factor) —
Factor to rescale the image pixel values by. bool, optional, defaults to self.do_normalize) —
Whether to normalize the image pixel values by image_mean and image_std. float or List[float], optional, defaults to self.image_mean) —
Mean to normalize the image pixel values by. float or List[float], optional, defaults to self.image_std) —
Standard deviation to normalize the image pixel values by. str or TensorType, optional) —
The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:np.ndarray.TensorType.TENSORFLOW or 'tf': Return a batch of type tf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCH or 'pt': Return a batch of type torch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPY or 'np': Return a batch of type np.ndarray.TensorType.JAX or 'jax': Return a batch of type jax.numpy.ndarray.str or ChannelDimension, optional, defaults to ChannelDimension.FIRST) —
The channel dimension format for the output image. If unset, the channel dimension format of the input
image is used. Can be one of:"channels_first" or ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last" or ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.ChannelDimension or str, optional) —
The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred
from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first" or ChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last" or ChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none" or ChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.Preprocess an image or batch of images to be used as input to a LeViT model.
( config )
Parameters
The bare Levit model outputting raw features without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
( pixel_values: FloatTensor = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) —
Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See
LevitImageProcessor.call() for details. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See hidden_states under returned tensors for
more detail. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (LevitConfig) and inputs.
last_hidden_state (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model.
pooler_output (torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state after a pooling operation on the spatial dimensions.
hidden_states (tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned when output_hidden_states=True is passed or when config.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple of torch.FloatTensor (one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, +
one for the output of each layer) of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width).
Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
The LevitModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, LevitModel
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> model = LevitModel.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 16, 384]( config )
Parameters
Levit Model with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled features), e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
( pixel_values: FloatTensor = None labels: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) —
Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See
LevitImageProcessor.call() for details. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See hidden_states under returned tensors for
more detail. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. torch.LongTensor of shape (batch_size,), optional) —
Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in [0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. If config.num_labels == 1 a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), If
config.num_labels > 1 a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy). Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (LevitConfig) and inputs.
torch.FloatTensor of shape (1,), optional, returned when labels is provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss.torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax).tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned when output_hidden_states=True is passed or when config.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple of torch.FloatTensor (one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, +
one for the output of each stage) of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also
called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.The LevitForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, LevitForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> model = LevitForImageClassification.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
tabby, tabby cat( config )
Parameters
LeViT Model transformer with image classification heads on top (a linear layer on top of the final hidden state and a linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the distillation token) e.g. for ImageNet. .. warning:: This model supports inference-only. Fine-tuning with distillation (i.e. with a teacher) is not yet supported.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
( pixel_values: FloatTensor = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.levit.modeling_levit.LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacherOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) —
Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See
LevitImageProcessor.call() for details. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See hidden_states under returned tensors for
more detail. bool, optional) —
Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. Returns
transformers.models.levit.modeling_levit.LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacherOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.levit.modeling_levit.LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacherOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (LevitConfig) and inputs.
torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Prediction scores as the average of the cls_logits and distillation_logits.torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Prediction scores of the classification head (i.e. the linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the
class token).torch.FloatTensor of shape (batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Prediction scores of the distillation head (i.e. the linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the
distillation token).tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned when output_hidden_states=True is passed or when config.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple of torch.FloatTensor (one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of
shape (batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer
plus the initial embedding outputs.The LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> model = LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher.from_pretrained("facebook/levit-128S")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
tabby, tabby cat